Celsys’s Sustainability
Basic Sustainability Policy
Our mission (our daily duty) is “Creating a more passionate world,” and our vision (the future we want to realize) is “The world is more vibrant when everyone’s passions are connected.” Celsys conducts its corporate activities based on these principles. In addition to supporting creators who engage in creative activities, we aim to enhance corporate value and contribute to the realization of a sustainable society by expanding people’s passions worldwide through the content created, and fostering new communities and connections that transcend generations, borders, and cultures.
Kei Narushima, President
CELSYS, Inc.

1. Our Approach to Sustainability and Related Initiatives
Celsys views addressing sustainability-related challenges not only as a means of reducing risks but also as an important management issue that can lead to revenue opportunities. From the perspective of enhancing corporate value over the medium-to-long term, we have established the following basic sustainability policy to actively and energetically tackle these challenges.
2. Governance
In January 2024, Celsys newly established the Sustainability Committee as a subordinate organization of the Board of Directors through a board resolution. The purpose of this committee is to focus on discussing and promoting our medium- to long-term sustainability strategy. The committee is chaired by the President, and its members include internal directors and division heads. Sustainability policies and measures are primarily driven by each division, and the progress of these initiatives is reported to the Board of Directors through the Sustainability Committee as necessary.
3. Strategy
(1) Overall Sustainability
Based on Celsys’s values (three values that drive passion), what we want to become, and an analysis of risks and opportunities involved in realizing them, we have identified materiality as key themes that the entire Celsys must prioritize for action. The materiality was approved at the Sustainability Committee meeting held in January 2024.
The “three values that drive passion” are as follows:

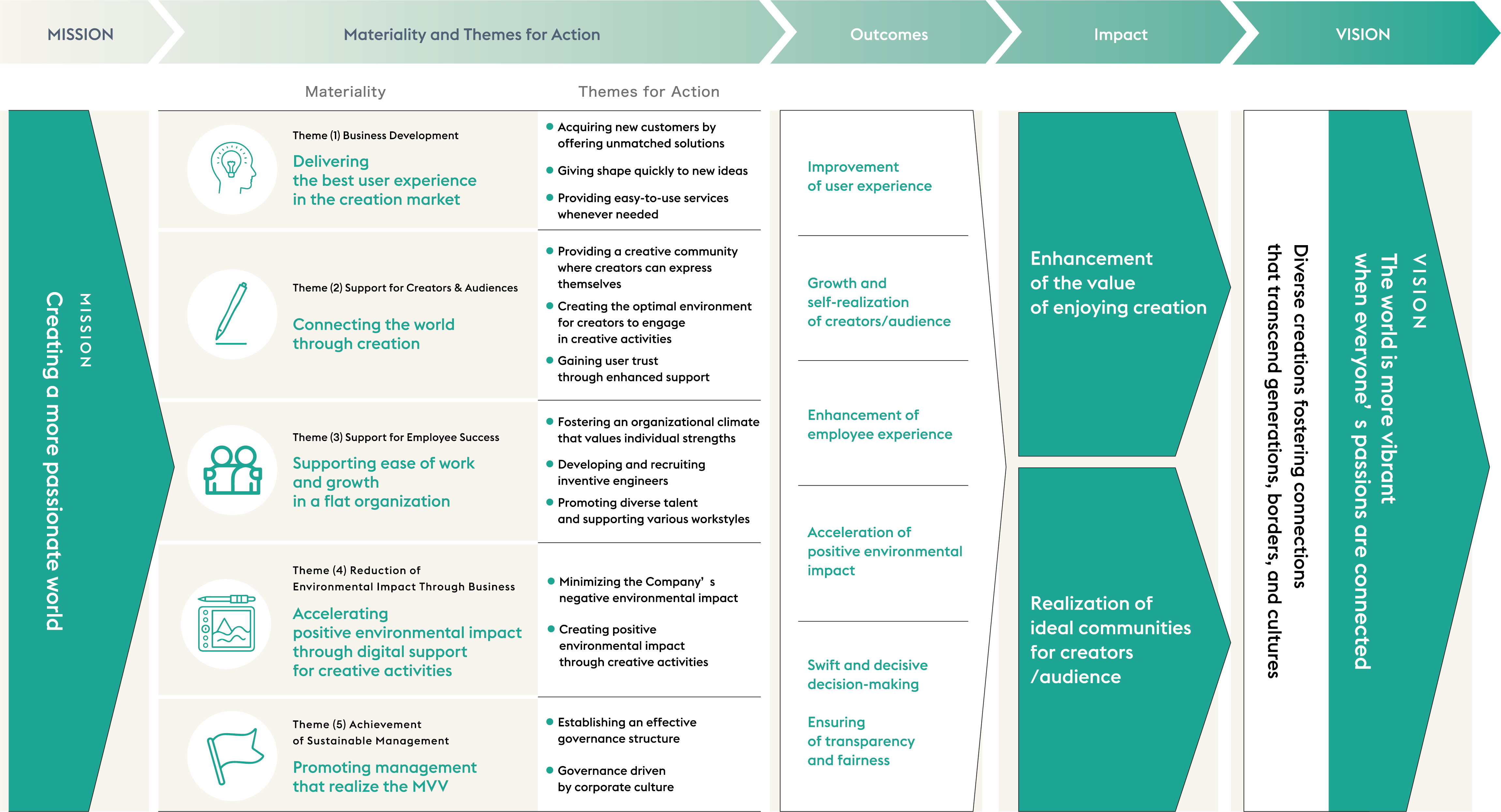
Materiality and Themes for Action Toward Realizing the Celsys’s Vision
(2) Policies on Human Resource Development, Including Ensuring Diversity, and Internal Environment Development
Celsys recognizes the importance of human resource development, including ensuring diversity, and internal environment development as stated in the materiality related to support for employee success, “supporting ease of work and growth in a flat organization.”
Basic Policies on Human Resource Development and Internal Environment Development
In today’s rapidly evolving era of technology, innovative organizations and individuals that can think flexibly without being bound by conventional wisdom are in high demand. Within this context, one of the key themes of Celsys’s human resource development is how to increase growth opportunities where individuals can leverage their strengths to take on and complete challenges. We aim for each employee to perform their work with passion and enjoyment while enhancing their professional expertise and technical skills.
We strive to expand our services both domestically and internationally, aiming to foster connections that transcend generations, borders, and cultures through diverse “creations.” It is therefore crucial to create a flat organizational climate in the workplace. In addition to supporting employees through various systems and initiatives, we will cultivate an organizational climate where each employee is encouraged to harness and complement one another’s strengths.
●Organizational Climate Reform
Celsys believes that philosophy-based management forms the foundation for creating a culture that evolves the organization. As part of our efforts toward organizational climate reform, in 2023, we redefined our philosophy system, which consists of our mission, vision, and values. Building upon this, we formulated a management policy aimed at implementing philosophy-based management.
●Recruitment and Development of Inventive Engineers
Celsys believes that the most important aspect of recruitment is hiring individuals who resonate with our philosophy and possess a deep understanding and respect for creative culture. To support the development of technical skills and growth, we have held internal technical study sessions and institutionalized a quarterly evaluation system to provide swift feedback on performance. Additionally, Celsys places emphasis on nurturing the next generation of talent, beyond just recruitment activities. Our industry-academia collaboration initiatives with universities have contributed to the recruitment of engineers.
●Promoting Diverse Talent and Supporting Various Workstyles
We prioritize designing organizations that thoughtfully combine individuals to generate new positive synergies. In terms of living places and workstyles, we operate flexible systems, and in April 2024, we introduced a new flextime system.
4. Risk Management
The Sustainability Committee manages risks related to promoting sustainability. Each division, in coordination with the Risk and Compliance Committee as necessary, drives the identification of individual risks and the formulation of response policies, which are then reported to the Sustainability Committee. The Sustainability Committee, in turn, reports these risks to the Board of Directors when necessary.
5. Indicators and Targets
(1) Overall Sustainability
We consider the following to be the monitoring indicators related to the materiality described in the strategy. For monitoring indicators that require targets to advance our initiatives, we will consider setting these targets in the future.
Materiality |
Themes for action |
Monitoring indicators |
|---|---|---|
Theme (1) Business Development |
・Acquiring new customers by offering unmatched solutions |
・Number of creator members |
Theme (2) Support for Creators & Audiences |
・Providing a creative community where creators can express themselves |
・Total number of units shipped |
Theme (3) Support for Employee Success |
・Fostering an organizational climate that values individual strengths |
・Ratio of female managers |
Theme (4) Reduction of Environmental Impact Through Business |
・Minimizing the Company’s negative environmental impact |
・The Company’s GHG emissions |
Theme (5) Achievement of Sustainable Management |
・Establishing an effective governance structure |
・Board of Directors attendance rate |
(2) Policy on Human Resource Development, Including Ensuring Diversity, and Internal Environment Development
Regarding ensuring the diversity of human capital, we continue proactive recruitment activities that do not depend on gender, nationality, or age. This includes actively promoting exceptional talent, including mid-career employees, to management positions. While believing that a certain number of female and foreign managers has been secured, we consider it important to increase their ratio through the planned development and promotion of core personnel. Furthermore, we are working to create an environment where all employees, with their diverse personalities and values, can find fulfillment in their work and have workstyles that align with their personal lifestyles and life stages, regardless of gender or age. Specifically, we have implemented initiatives such as the introduction of remote work, the adoption of a flextime system, and the introduction and promotion of various leave systems, including childcare leave.
Basic Information on Diversity
Indicator |
Performance |
Remarks (Scope of Data Collection) |
|---|---|---|
Number of employees by gender |
Male: 152, Female: 127 |
Consolidated; including temporary employees and those on leave |
Status of new graduate employees and mid-career employees |
New graduate: Male: 40, Female: 15 |
Consolidated |
Gender pay gap |
72.4% |
Consolidated |
Average length of service |
Male: 7 years and 11 months, |
Consolidated |
Ratio of female managers |
33.3% |
Consolidated |
Ratio of female officers |
9.1% |
Non-consolidated; not including Corporate Officers |
Number of foreign employees |
35 (Percentage of total: 12.5%) |
Consolidated |
Ratio of foreign managers |
3.9% |
Consolidated |
*As of December 31, 2024
Basic Information on Childcare Leave and Paid Leave
Indicator |
Performance |
Remarks (Scope of Data Collection) |
|---|---|---|
Paid leave utilization rate |
70.3% |
Consolidated |
Female childcare leave utilization rate |
100% |
Consolidated |
Male childcare leave utilization rate |
25% |
Consolidated |
*From the March 2025 securities report
6. Response to Climate Change (Information Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations)
(1) Approach to Climate Change
Celsys recognizes that contributing to the realization of a sustainable society and enhancing corporate value over the medium-to-long term are important management issues. In line with our basic sustainability policy, we are actively and proactively addressing these issues. In particular, regarding sustainability challenges related to climate change, we are organizing our approach and advancing initiatives in accordance with each theme of TCFD information disclosure.
(2) Governance
To promote sustainability initiatives, including those related to climate change, Celsys has established the Sustainability Committee. Under the supervision of the President, who serves as the committee chair, this committee examines action policies related to sustainability, including climate change, and reports progress to the Board of Directors as necessary. The Board of Directors deliberates on the reported content accordingly.
(3) Strategy
Celsys has identified “accelerating positive environmental impact through digital support for creative activities” as the materiality related to reduction of environmental impact through business. We consider addressing environmental challenges, including climate change, important. Accordingly, Celsys has been conducting scenario analyses in line with TCFD recommendations to understand the impact of climate change-related transition risks and physical risks on our business activities and to consider and formulate a business strategy that can respond to uncertain future conditions.
In the scenario analysis conducted this time, we considered two scenarios: a 4°C scenario, where the global temperature rises by 4°C compared to pre-industrial levels, and a 1.5°C scenario, where efforts are made to keep the temperature rise below 2°C, centering around 1.5°C. We qualitatively examined and analyzed risks and opportunities related to climate change as of 2030 under these scenarios. Going forward, we plan to conduct quantitative analyses to further visualize the impact on our business.
|
4℃ scenario |
1.5℃ scenario |
|---|---|---|
Worldviews |
・A world where the global average temperature rises by approx. 4°C compared to pre-industrial levels by 2100 |
・A world where the global average temperature rise is kept to approx. 1.5°C compared to pre-industrial levels by 2100 |
Reference scenarios |
IEA WEO 2023/2019 STEPS |
IEA WEO 2023/2019 NZE/SDS |
●4°C Scenario Analysis
In the analysis under the 4°C scenario, we have identified the potential for an increased risk of damage to our bases due to the intensification and increased frequency of extreme weather events. If a base is damaged, losses are expected to occur due to business shutdowns and damage to assets. Therefore, we plan to explore quantitative analysis moving forward.
●1.5°C Scenario Analysis
In the analysis under the 1.5°C scenario, we have identified substantial potential impacts on our operations due to the transition to a decarbonized society, including the imposition of carbon taxes, rising electricity prices driven by increased demand for renewable energy, and various policies and regulations related to renewable energy and energy conservation. We plan to conduct a quantitative analysis of how these risks may affect the Company in the future.
On the other hand, we anticipate that efforts toward a decarbonized society may lead to increased demand for energy-saving and resource-efficient products. Providing products that meet such demand has been identified as an opportunity for the Company. Going forward, we will promote initiatives aimed at reducing environmental impact through our business to “accelerate positive environmental impact.”
Risk items |
Time of materialization |
Financial impact (qualitative) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
4℃ |
1.5℃ |
|||||
Risk |
Transition |
Carbon pricing (carbon tax) |
A carbon tax will be imposed on the CO2 emissions from Scope 1 and 2 business activities, leading to an increase in running costs. |
Medium to long term |
ー |
Medium |
Carbon emission targets/policies |
Investment costs for zero-emission and resilience enhancement projects of data centers will be passed on to service fees, increasing costs. |
Short to long term |
Small |
Medium |
||
Renewable energy policies |
With the strengthening of renewable energy policies, if renewable energy systems are installed in rental properties, the investment costs will be reflected in rental fees, increasing costs. |
Medium to long term |
Small |
Medium |
||
Changes in energy costs |
Rising demand for renewable energy and the costs of capital expenditures will lead to higher electricity prices, increasing running costs. |
Medium to long term |
ー |
Medium |
||
Changes in reputation among investors |
If environmental information disclosure is inadequate, concerns about climate resilience may lead to reduced investment, making it difficult to secure financing. |
Medium to long term |
Small |
Medium |
||
Physical |
Intensification of extreme weather (typhoons, heavy rain, landslides, storm surges, etc.) |
Increased severity of weather disasters may lead to damage to company bases or disruption of supply chains, resulting in losses due to business shutdowns or reduced sales. |
Medium to long term |
Medium |
Small |
|
An increase in disasters will lead to higher fire insurance premiums, resulting in increased costs. |
Short to long term |
Medium |
Small |
|||
Opportunity |
Carbon emission targets/policies |
The demand for applications and software that consume less energy during use will increase. |
Medium to long term |
Small |
Medium |
|
Forest protection policies |
As paperless practices advance from the perspective of protecting forest resources that sequester CO2, the demand for software in creative fields such as manga and illustration will further grow. Additionally, the demand for and usage of digital content will also increase. |
Short to long term |
Small |
Large |
||
Spread of renewable energy and energy-saving technologies |
As more energy-efficient devices become widespread, sales of licenses for applications installed on those devices will increase. |
Medium to long term |
Small |
Medium |
||
Changes in customer behavior |
As the market demands GHG emission reductions throughout product life cycles, sales of intangible goods with low life-cycle GHG emissions will increase. |
Medium to long term |
Small |
Medium |
||
Definition of time of materialization: “Short term” means 0-3 years; “Medium term” means 4-10 years; and “Long term” means 11-30 years.
Definition of financial impact: “Large” means significant impact on the business; “Medium” means impact on part of the business; “Small” means minimal impact on the business; and “―” means no impact.
(4) Risk Management
Celsys identifies and assesses climate-related risks through the Sustainability Committee. Each division involved with the identified risks and opportunities implements and promotes measures to address them. The Sustainability Committee monitors the progress of these initiatives and manages climate-related risks. Matters concerning these risks are reported to the Board of Directors by the Sustainability Committee as necessary.
Additionally, climate-related risks identified and assessed by the Sustainability Committee are integrated with other risks in coordination with the Risk and Compliance Committee.
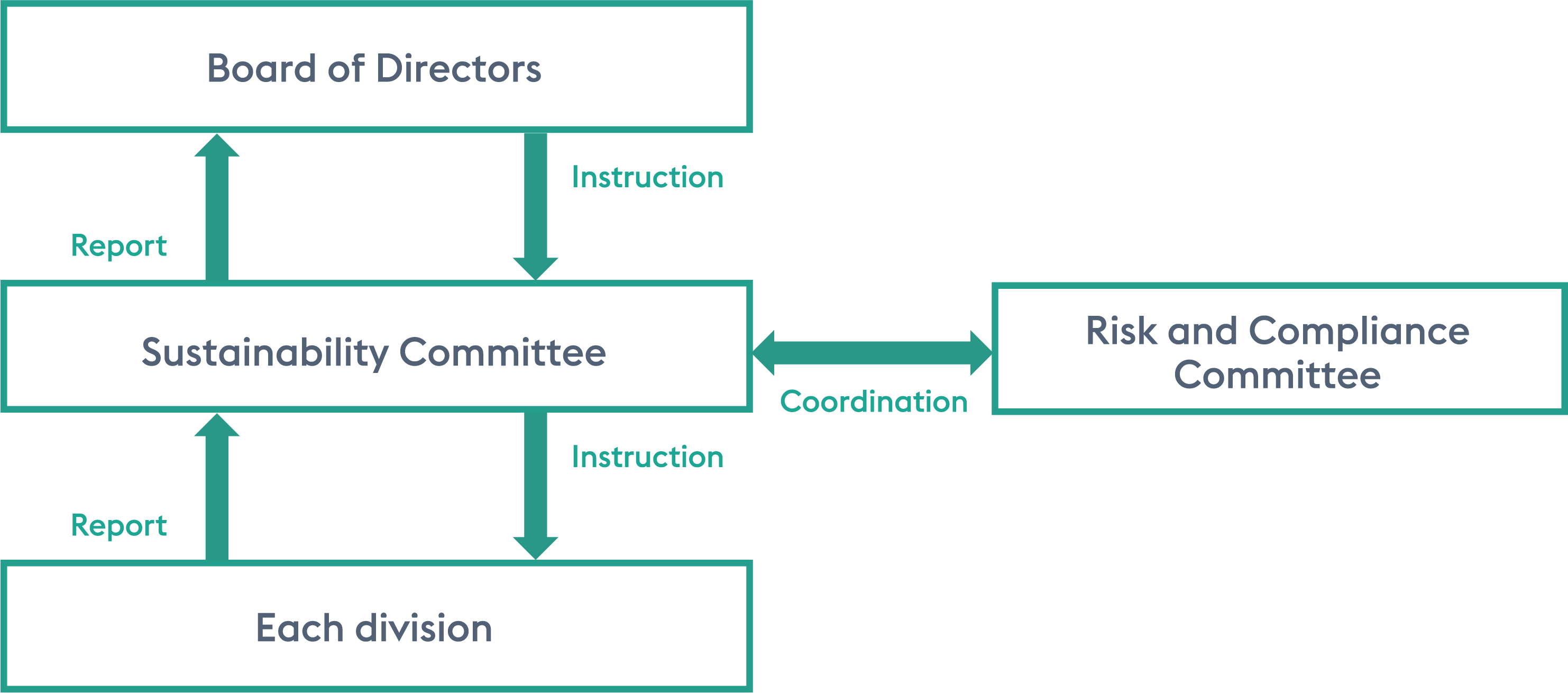
(5) Indicators and Targets
Celsys has calculated the GHG emissions resulting from our business activities, with the results as follows:
|
2023 |
|
|---|---|---|
GHG emissions [tCO2] |
||
Scope1 |
3.3 |
|
Scope2 |
Location-based |
124.2 |
Market-based |
85.4 |
|
Total of Scope 1 and 2* |
88.7 |
|
*1: Scope 1 + Scope 2 (Market-based)
Moving forward, we will consider setting reduction targets for Scope 1 and 2 emissions, as well as calculating and setting reduction targets for Scope 3, in order to contribute to the realization of a sustainable society.


